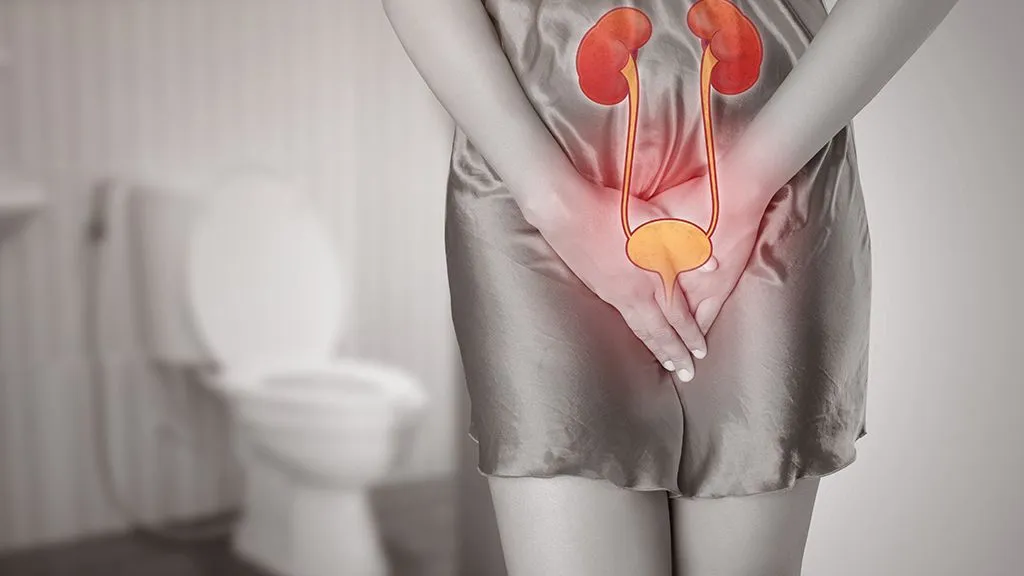
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is a common bacterial infection that affects the urinary system of women. It usually affects the bladder and urethra, resulting in symptoms such as pain or burning during urination, frequent impulses to urinate, and lower abdomen discomfort.
UTIs are more common in females due to their anatomy, where the shorter urethra makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. As per Dr Rachna, a renowned gynaecologist in Rohini, Delhi, most UTIs are treatable with medicines. Read on this article to know more about Urinary Tract Infection in Females
What is a Urinary Tract Infection?
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when bacteria infect any component of the urinary system, such as the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra. The majority of UTIs involve the lower urinary system, particularly the bladder and urethra.
Women have a higher risk of UTIs compared to men. When an infection is confined to the bladder, it can cause pain and discomfort. However, if a UTI spreads to the kidneys, it can lead to more serious health complications.
Gynaecologist in Delhi typically treat UTIs with antibiotics. Furthermore, there are precautions you may take to lower your chances of acquiring a UTI in the first place.
Symptoms of urinary tract infection
A UTI leads to inflammation in the lining of your urinary tract, which can result in the following issues:
- Pain in your side, abdomen, pelvic area, or lower back.
- Lower pelvic pressure.
- Urine that appears cloudy and has a foul smell.
- Urinary leakage (incontinence).
- You Need to urinate frequently.
- Sudden, strong urges to urinate (urge incontinence).
- Painful urination (dysuria).
- Blood in your urine (hematuria).
What causes UTIs?
The most common UTIs primarily affect women and typically involve the bladder and urethra.
- Delaying urination when you feel the need or not fully emptying your bladder can cause harmful bacteria to accumulate in your bladder.
- Kidney stones can block your urinary tract, disrupting the normal flow of urine.
- Diabetes can elevate sugar levels in your blood and urine. High sugar levels in urine can foster bacterial growth.
- Using a bladder or urinary catheter recently can also contribute to urinary tract issues. These flexible tubes drain urine from the bladder into a collection bag, commonly used post-surgery when normal urination is not possible.
Bladder infection, often caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a bacteria commonly found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is the most common type of UTI. Other bacteria, however, could be at blame.
Sexual activity can sometimes lead to a bladder infection, although it’s not necessary to be sexually active to develop one. Women are at greater risk due to their anatomy—specifically, the proximity of the urethra to the anus and the short distance between the urethral opening and the bladder. This facilitates the entry of bacteria from the anus into the urethra and subsequent journey to the bladder.
Treatments of UTI infection in Delhi
Antibiotics are the main treatment for UTIs. You might have noticed that you start feeling better on the second day of taking antibiotics, even though your doctor prescribed a five-day course of medicines.
UTIs are typically treated with the following medicines, take only if prescribed and recommended by your doctor:
– Doxycycline
– Quinolones such as Ciprofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin combined with Phenazopyridine, Ofloxacin combined with Flavoxate, Levofloxacin, and Ofloxacin
– Cephalosporins like Ceftriaxone
– Nitrofurantoin
– Clotrimazole
– Amoxicillin
These antibiotics are prescribed based on the specific bacteria causing the infection and other factors like allergies and previous antibiotic use. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your doctor to ensure the infection is fully treated and to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Preventive measures
Here are some self-care measures you can follow for UTI:
- Use a heating pad or hot water bottle to alleviate discomfort and pain.
- Drink plenty of water, aiming for 8-12 glasses daily.
- Urinate as soon as you feel the need; holding urine in the bladder can promote bacterial growth.
- Wear cotton underwear and loose-fitting clothing to allow air circulation and keep the area dry.
- Take Vitamin C supplements; it increases urine acidity, making it harder for bacteria to thrive.
- Avoid chocolate, citrus fruits, carbonated drinks, and caffeine, as these can irritate the bladder lining and create a favourable environment for bacteria to survive.
Complications in UTI infections for females
If not treated, UTIs can persist for months. There’s also a significant risk of the infection spreading to other areas like the kidneys, causing a kidney infection. This can result in recurring infections, particularly among women. In rare instances, untreated UTIs can progress to sepsis, a serious blood infection that can lead to severe complications. Early treatment is important to prevent these potential complications.
Gynaecologist in Rohini for UTI treatment
If you notice any symptoms of UTI, it’s important to see your doctor promptly. Specialists who can diagnose and treat UTIs include:
– Gynaecologists
– Urologists
These doctors have the expertise to provide appropriate care and treatment for urinary tract infections. Book a consultation with Dr Rachna, leading gynaecologist in Delhi with years of experience in this field.
Maintaining good hygiene is essential for preventing UTIs, particularly for individuals with a vagina since their urethra is shorter. During menstruation, it’s advisable to change sanitary products like pads and tampons regularly. Avoid using any vaginal deodorants as well. These practices can help reduce the risk of urinary tract infections.